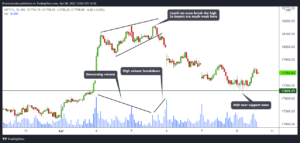
Technical analysis is a powerful tool that is used by traders and investors to identify patterns in the market and make informed decisions. One of the most popular patterns in technical analysis is the wedge pattern. Wedge patterns are formed when the price of an asset moves in a tight range between two sloping trend lines, indicating a potential reversal of the current trend. There are two types of wedge patterns: rising and falling.
Understanding these patterns is essential for traders and investors who want to master technical analysis and make profitable trades. In this post, we will break down the secrets of rising and falling wedges, including how to identify them, what they signify, and how to use them to make informed trading decisions. Whether you are new to technical analysis or an experienced trader, this guide will help you unlock the power of wedge patterns and take your trading to the next level.
1. Introduction to wedge patterns in technical analysis
In the world of technical analysis, there are various patterns that traders and investors use to predict market trends and make informed trading decisions. One such pattern that has gained significant popularity is the wedge pattern.
Wedge patterns are powerful tools that can provide valuable insights into future price movements. They are formed when the price of an asset consolidates between two converging trendlines, creating a triangular shape. These trendlines can either be sloping upwards, known as a rising wedge, or sloping downwards, known as a falling wedge.
The rising wedge pattern typically occurs during an uptrend and is characterized by a narrowing range between higher highs and higher lows. This formation suggests that the buying pressure is weakening, and a potential reversal or correction may be on the horizon. Traders often look for a break below the lower trendline as a signal to sell or go short.
On the other hand, the falling wedge pattern is typically observed during a downtrend and is characterized by a narrowing range between lower highs and lower lows. This formation suggests that the selling pressure is weakening, and a potential trend reversal or bullish breakout may occur. Traders often look for a break above the upper trendline as a signal to buy or go long.
It’s important to note that wedge patterns are not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with other technical indicators and analysis methods to validate potential trading opportunities. Additionally, it’s crucial to consider the overall market conditions, news events, and other factors that may influence price movements.
By understanding and mastering wedge patterns in technical analysis, traders and investors can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and improve their ability to identify potential trend reversals and breakouts. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of rising and falling wedges, exploring their characteristics, interpretation, and practical application in real-world trading scenarios.
2. Understanding the anatomy of a rising wedge pattern
To effectively analyze and trade wedge patterns, it is crucial to understand the anatomy of each specific pattern. In this section, we will delve into the rising wedge pattern and unravel its secrets.
A rising wedge pattern is a powerful technical formation that often signals a potential reversal in an uptrend. Visually, it resembles a narrowing triangle or a wedge shape, with both trend lines converging as the price moves higher. The upper trend line connects the swing highs, while the lower trend line links the swing lows.
One key characteristic of a rising wedge is that both trend lines slope in an upward direction, indicating increasing buying pressure. However, beneath the surface, the buying pressure is slowing down, and the price is gradually losing momentum.
As the pattern develops, traders should pay attention to the volume levels. Ideally, volume should diminish as the price approaches the apex of the wedge, indicating a lack of conviction from buyers. This divergence between price and volume strengthens the bearish signal generated by the pattern.
Another important aspect to consider is the duration of the pattern. A rising wedge typically forms over several weeks or months, allowing traders to observe the gradual compression of price within the narrowing boundaries. The longer the pattern takes to form, the stronger the potential reversal signal becomes.
Traders can anticipate a breakout from the rising wedge pattern by monitoring the price action near the apex. A breakdown below the lower trend line confirms the pattern’s completion and suggests a potential trend reversal to the downside. It is crucial to wait for a clear break before entering a short position, as false breakouts can occur.
To enhance the accuracy of your analysis, it is advisable to combine the rising wedge pattern with other technical indicators or chart patterns. For example, a bearish divergence in oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can provide additional confirmation of a potential reversal.
In conclusion, mastering the understanding of the anatomy of a rising wedge pattern is essential for successful technical analysis. By recognizing the visual characteristics, monitoring volume patterns, and waiting for a confirmed breakout, traders can effectively use this pattern to identify potential trend reversals and make informed trading decisions.
3. Identifying key characteristics of a rising wedge pattern
Identifying key characteristics of a rising wedge pattern is essential for traders and investors who want to make informed decisions in the realm of technical analysis. A rising wedge pattern can provide valuable insights into potential future price movements and trend reversals.
The first characteristic to look for in a rising wedge pattern is the formation of converging trendlines. These trendlines are drawn by connecting the higher swing highs and higher swing lows. As the pattern develops, the price action becomes confined within these trendlines, creating a narrowing range.
Another important characteristic of a rising wedge pattern is the upward slope of the lower trendline, which is usually steeper compared to the upper trendline. This indicates that buying pressure is gradually weakening, while sellers are gaining strength. As a result, the price tends to make higher highs but with less upward momentum, creating a bearish divergence between price and momentum indicators.
Volume analysis plays a crucial role in identifying a rising wedge pattern. Typically, volume diminishes as the pattern unfolds, signaling a decrease in market participation. This decline in volume confirms the loss of buying interest and further supports the bearish implications of the pattern.
Traders should also pay attention to the duration of the pattern. A rising wedge pattern tends to form over a relatively longer period compared to other chart patterns. This extended formation adds significance to its potential reversal implications.
Overall, mastering the identification of key characteristics of a rising wedge pattern can empower traders to anticipate potential trend reversals and take advantage of profitable trading opportunities. However, it is important to combine this analysis with other technical indicators, risk management strategies, and market context to make well-informed trading decisions.
4. Interpreting the psychology behind a rising wedge pattern
Interpreting the psychology behind a rising wedge pattern is crucial in understanding its significance in technical analysis. A rising wedge is a powerful chart pattern that indicates a potential reversal in an uptrend. It is formed by converging trendlines, where the slope of the lower trendline is steeper than the upper trendline. This creates a narrowing price range, resembling a triangle with a bullish bias.
From a psychological standpoint, a rising wedge pattern represents a battle between buyers and sellers. As the price continues to make higher highs and higher lows, buyers are still in control, pushing the price higher. However, the narrowing range signals a decrease in buying momentum and an increase in selling pressure.
Traders who are aware of the psychology behind this pattern can gain valuable insights into market sentiment. The rising wedge suggests that buyers are becoming exhausted, and sellers are gradually gaining strength. It reflects a sense of indecision and a potential shift in market dynamics.
As the price approaches the apex of the rising wedge, traders should be cautious, as it often precedes a significant reversal. The breakout from the lower trendline confirms the pattern completion and indicates a shift in power from buyers to sellers. This breakdown can trigger a sharp and rapid decline in price, leading to potential selling opportunities or a transition to a downtrend.
Understanding the psychology behind a rising wedge pattern allows traders to anticipate market movements, make informed decisions, and potentially profit from these price reversals. It is essential to combine this analysis with other technical indicators and risk management strategies to maximize trading success.
5. Trading strategies for rising wedge patterns
Trading strategies for rising wedge patterns can be highly effective when properly executed. A rising wedge pattern is characterized by a series of higher highs and higher lows, with converging trendlines forming an upward slope. This pattern indicates a potential reversal in the current uptrend and a possible downward price movement.
One popular trading strategy for rising wedge patterns is the breakout strategy. Traders wait for a confirmed breakout below the lower trendline, signaling a potential trend reversal. This breakout is often accompanied by increased selling pressure and a surge in volume, further validating the pattern’s reliability.
Once the breakout is confirmed, traders can enter short positions, aiming to profit from the anticipated downward price movement. Setting a stop-loss above the upper trendline helps manage risk in case the breakout turns out to be a false signal.
Another trading approach is the retest strategy, which involves waiting for a pullback or retest of the broken lower trendline after the breakout. This retest provides an opportunity to enter short positions at a better price, as the price often bounces off the broken trendline before resuming its downward trajectory.
It’s essential to monitor other technical indicators, such as momentum oscillators or volume indicators, to confirm the validity of the rising wedge pattern and strengthen the trading strategy. Additionally, incorporating proper risk management techniques, such as setting profit targets and trailing stop-loss orders, can help maximize potential gains and limit potential losses.
Remember, no trading strategy is foolproof, and it’s crucial to practice using demo accounts or paper trading before implementing these strategies with real money. Furthermore, staying updated with market news and continuously honing technical analysis skills will enhance your ability to identify and trade rising wedge patterns successfully.
6. Unveiling the secrets of falling wedge patterns
Falling wedge patterns are a powerful tool in technical analysis that can provide valuable insights into potential market trends. These patterns are characterized by a narrowing range between two converging trendlines, with the upper trendline sloping downwards while the lower trendline slopes upwards.
One of the secrets of falling wedge patterns is that they often signal a bullish reversal. This means that after a prolonged downtrend, the falling wedge pattern indicates that the selling pressure is gradually decreasing and buyers are starting to gain control. As the price continues to make lower lows and higher lows within the wedge, it suggests that the market is becoming less bearish and more balanced.
Another secret of falling wedge patterns is that they can provide precise entry and exit points for traders. The breakout from the upper trendline of the wedge is seen as a bullish signal, indicating that the price is likely to reverse and start an upward trend. Traders can use this breakout as a buying opportunity, placing a stop-loss order below the lower trendline to manage risk.
Additionally, falling wedge patterns can also provide valuable insights into potential price targets. Traders often measure the height of the wedge from the breakout point to the highest point within the pattern, and then project this distance upwards from the breakout point. This can give an estimated target for the price movement after the breakout.
However, it’s important to note that not all falling wedges lead to a bullish reversal. Sometimes, the price can break downwards from the pattern, indicating a continuation of the downtrend. Therefore, it’s essential to use other technical indicators and confirmatory signals to validate the potential reversal suggested by the falling wedge pattern.
In conclusion, falling wedge patterns are a powerful tool in technical analysis that can help traders identify potential bullish reversals and provide precise entry and exit points. By understanding the secrets of falling wedges, traders can enhance their analysis and make more informed trading decisions.
7. Key characteristics of a falling wedge pattern
When it comes to technical analysis, understanding the different patterns can give you a valuable edge in predicting price movements. One such pattern that traders often encounter is the falling wedge pattern. This pattern is characterized by a series of lower highs and lower lows, forming a converging trendline.
The key characteristics of a falling wedge pattern are as follows:
1. Converging trendlines:
The falling wedge pattern is formed by two trendlines that are moving towards each other in a downward direction. The upper trendline connects the lower highs, while the lower trendline connects the lower lows. This creates a wedge-like shape on the price chart.
2. Gradual price decline:
Within the falling wedge pattern, the price tends to gradually decline, forming the lower lows along the lower trendline. This indicates a slowing down of the selling pressure and a potential shift in market sentiment.
3. Decreasing volume:
As the falling wedge pattern develops, the trading volume generally decreases. This decrease in volume indicates a lack of interest or participation from market participants, further suggesting a potential reversal in the near future.
4. Bullish breakout:
The falling wedge pattern is typically considered a bullish reversal pattern. Traders often anticipate a breakout above the upper trendline, signaling a potential trend reversal from bearish to bullish. This breakout is usually accompanied by an increase in volume, confirming the validity of the pattern.
5. Price target:
To determine a price target after the breakout, measure the height of the widest part of the wedge and project it upwards from the breakout point. This can provide an estimation of the potential price move after the pattern is confirmed.
By recognizing the key characteristics of a falling wedge pattern, traders can strategically position themselves to take advantage of potential trend reversals and capitalize on profitable trading opportunities. However, it is essential to remember that technical analysis should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis and risk management strategies to make informed trading decisions.
8. The psychology behind a falling wedge pattern
Understanding the psychology behind a falling wedge pattern is crucial in mastering technical analysis. This pattern is formed when the price of an asset is gradually declining, but at a slower pace than the slope of the lower trendline. As a result, the price forms a series of lower highs and lower lows, creating a narrowing wedge shape.
The psychology behind a falling wedge pattern is rooted in market sentiment and investor behavior. During a downtrend, investors may become pessimistic and hesitant to buy, leading to a decrease in demand. However, as the price continues to decline, some investors start perceiving it as undervalued or reaching a point of exhaustion. This shift in perception can trigger buying interest and gradually turn the tide.
One reason why a falling wedge pattern is considered bullish is the presence of higher lows. Despite the overall downward movement, each subsequent low is higher than the previous one, indicating diminishing selling pressure. This can be attributed to a combination of profit-taking by short sellers and new buyers entering the market at lower levels.
Another psychological factor at play is the concept of support and resistance. The lower trendline of the falling wedge pattern acts as a support level, preventing the price from falling further. As the price approaches this support level multiple times, traders who were previously selling may now start buying to capitalize on potential price reversals.
Additionally, the narrowing range of the falling wedge pattern creates a sense of compression, building up potential energy. Traders anticipate a breakout in the direction opposite to the slope of the wedge, expecting a bullish reversal. This anticipation can further fuel buying interest and contribute to the pattern’s bullish nature.
In summary, the psychology behind a falling wedge pattern involves a shift in market sentiment, diminishing selling pressure, and the anticipation of a bullish reversal. By understanding these psychological factors, traders can effectively identify and interpret falling wedge patterns to make informed trading decisions.
9. Trading strategies for falling wedge patterns
When it comes to trading strategies for falling wedge patterns, there are a few key approaches that can help maximize your potential for profit.
First and foremost, it’s important to understand the characteristics of a falling wedge pattern. This pattern typically forms during a downtrend, signaling a potential reversal in the market. The wedge is formed by converging trendlines, with the upper trendline sloping downward at a steeper angle than the lower trendline.
One common strategy for trading falling wedge patterns is to wait for a breakout above the upper trendline. This breakout typically indicates a shift in market sentiment and can be a strong buy signal. Traders may set a buy order slightly above the upper trendline to capture the potential upward movement.
Another approach is to wait for a pullback towards the lower trendline. This pullback can provide an opportunity to enter a trade at a more favorable price. Traders may set a buy order near the lower trendline with a stop-loss order placed just below it to manage risk.
Additionally, it can be beneficial to combine the falling wedge pattern with other technical indicators or chart patterns to confirm the signal. For example, traders may look for bullish reversal candlestick patterns or bullish divergence on oscillators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
As with any trading strategy, it’s important to practice proper risk management and have a clear exit plan in place. This can include setting profit targets or using trailing stop-loss orders to protect gains. It’s also essential to stay updated on market news and be aware of any potential factors that could impact the trade.
By mastering trading strategies for falling wedge patterns and effectively combining them with other technical analysis tools, traders can increase their chances of success in the market and uncover the secrets of this powerful chart pattern.
10. Tips for mastering wedge patterns in technical analysis
When it comes to technical analysis, mastering wedge patterns can be a valuable tool in identifying potential market trends and making informed trading decisions. Wedge patterns, characterized by converging trend lines, can provide key insights into the direction and strength of price movements. Here are some tips to help you master wedge patterns in technical analysis.
1. Understand the types of wedge patterns:
Wedge patterns can be classified into two main types – rising wedges and falling wedges. Rising wedges are formed when the price consolidates between upward sloping trend lines, indicating a potential reversal from an uptrend. Falling wedges, on the other hand, occur when the price consolidates between downward sloping trend lines, suggesting a potential reversal from a downtrend. Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of each type to accurately identify and interpret wedge patterns.
2. Pay attention to volume:
Volume plays a crucial role in confirming wedge patterns. In a rising wedge, declining volume as the price reaches higher highs suggests weakening buying pressure, indicating a potential bearish reversal. Conversely, in a falling wedge, declining volume as the price reaches lower lows suggests diminishing selling pressure, signaling a potential bullish reversal. Analyzing volume alongside wedge patterns can enhance the accuracy of your analysis.
3. Wait for confirmation:
While wedge patterns can provide valuable insights, it’s important to wait for confirmation before making any trading decisions. Look for a breakout or breakdown from the wedge pattern, accompanied by increased volume, to confirm the validity of the pattern. This confirmation can help you avoid false signals and increase the probability of successful trades.
4. Consider timeframes:
Wedge patterns can appear on different timeframes, from intraday charts to weekly or monthly charts. Keep in mind that the significance of a wedge pattern may vary depending on the timeframe. For shorter timeframes, wedge patterns may indicate temporary price reversals or consolidations, while on longer timeframes, they can signify more significant trend reversals. Adjust your trading strategy accordingly based on the timeframe you are analyzing.
5. Combine with other technical indicators:
To strengthen your analysis, consider combining wedge patterns with other technical indicators. Oscillators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can provide additional confirmation or divergence signals. Additionally, incorporating support and resistance levels or Fibonacci retracement levels can further validate the potential price movements suggested by the wedge pattern.
By following these tips and gaining experience through practice, you can enhance your ability to identify and interpret wedge patterns in technical analysis. Mastering this valuable tool can contribute to your overall trading success and help you make more informed decisions in the dynamic world of financial markets.
Mastering Double Top and Double Bottom Chart Patterns in Technical Analysis
We hope you found our blog post on mastering wedge patterns in technical analysis informative and insightful. Understanding the secrets of rising and falling wedges can greatly enhance your ability to predict market trends and make informed trading decisions.
By mastering these patterns, you can gain a competitive edge in the world of technical analysis. Remember to practice and analyze real-time charts to sharpen your skills. We wish you success in your trading journey, and may your wedge patterns always lead you to profitable trades!
FAQ
Are there any drawbacks or limitations to relying solely on wedge patterns?
Yes, wedge patterns can sometimes produce false signals, and relying solely on them without considering other factors may lead to poor trading decisions. It's essential to use them as part of a comprehensive trading strategy.
Do wedge patterns work in all market conditions?
Wedge patterns can be effective in various market conditions, but like any technical analysis tool, they are not foolproof. It's crucial to consider the broader market context and use additional analysis to increase the reliability of signals.
How do I manage risk when trading based on wedge patterns?
Implement risk management strategies such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing. Determine your risk tolerance before entering a trade and be prepared to exit if the market moves against your expectations.